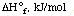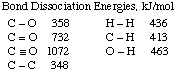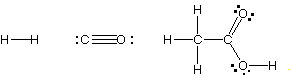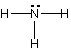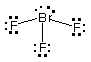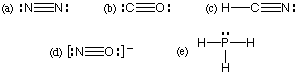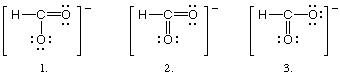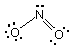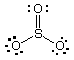CHEMISTRY 1P80 Final Exam 1998
(Solutions to numerical questions are given in
abbreviated form).
1. Short Calculations (20 marks)
(a) (3 marks) A sample was analyzed for the percentage of
alum, KAl(SO4)2. The sample was dissolved in
water. Excess BaCl2 was added to precipitate
BaSO4, and the barium sulfate was filtered and weighed. If
0.3218 g of sample yielded 0.2844 g of BaSO4, what is the
% KAl(SO4)2 in the sample? The net ionic
equation for the reaction is
Ba2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq)
---> BaSO4 (s)
|
BaCl2 208.2 g/mol
|
BaSO4 233.4 g/mol
|
KAl(SO4)2 258.2 g/mol
|
Remember that there are two sulfates in every
mole of alum.
Answer: 48.88%
(b) (3 marks) A bottle of barium chloride,
BaCl2, states that it is 98.5% pure (i.e., 98.5% of the
substance in the bottle is BaCl2 ). What mass must be
taken from the bottle to make 5.00 x 102 mL of a solution
whose chloride ion concentration is 0.150 M?
Molar mass: BaCl2 208.2 g/mol
7.808 grams of pure BaCl2 is needed, but
each gram of what is in the bottle contains only 0.985 grams of
BaCl2.
Therefore 7.808 g BaCl2 x (1 g from bottle / 0.985 g
BaCl2) = 7.93 g to weigh out.
(c) (4 marks) Consider the following data:
|
Compound
|
|
|
CO2 (g)
|
-393.5
|
|
H2O (l)
|
-285.8
|
|
CH3OH (l)
|
-239.1
|
(i) (1 mark) Write the balanced equation for the combustion
of CH3OH.
CH3OH + 1.5 O2 --->
CO2 + 2 H2O
(ii) (1 mark) The standard enthalpy of formation for
gaseous oxygen is not given in the above Table. Why not? What is it
for oxygen?
It doesn't need to be given because it is defined
to be zero for any element in its standard state.
(iii) (2 marks) Use the data given and calculate the molar
heat of combustion of liquid CH3OH.
Use the equation in part (i) and Hess's Law to
obtain -726 kJ/mol for the molar enthalpy of combustion of
methanol.
(d) (4 marks) Calculate the molarity of a sulfuric acid
solution whose density is 1.198 g/cm3, containing 27.0%
H2SO4 by weight. The molar mass of
H2SO4 is 98.1 g/mol.
Assume one liter of solution and find the moles of
sulfuric acid in it:
(1.000 L sol'n) x (1000 cm3/L) x (1.198 g
sol'n/cm3 sol'n) x (27.0 g H2SO4 /
100 g sol'n)
= 323.5 g H2SO4 in one liter
= 3.30 mol/L
(e) (3 marks) A 185-g piece of metal alloy, initially at
100.0 oC, is dropped into 265 g of water at 15.5
oC. When the system comes to thermal equilibrium, the
temperature is 24.1 oC. What is the specific heat capacity
of the metal? The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184
J/g.K.
Answer: 0.679 J/g.K
(f) (3 marks) Sodium azide, NaN3, is the
compound that decomposes to inflate automobile air bags. It is made
from nitrous oxide, sodium, and ammonia according to the following
reaction:
3 N2O + 4 Na + NH3 ---> NaN3 +
3 NaOH + 2 N2
If 16.2 g of NaN3 is obtained by the reaction of 24.00
g of sodium with excess ammonia and nitrous oxide, what is the %
yield?
|
NaN3 65.0 g/mol
|
NH3 17.03 g/mol
|
24.00 g of sodium can produce 16.96 g of NaN3 when
reacted with excess ammonia. Therefore the % yield is 95.5 %
2. (10 marks)
(a) 6 marks. Consider these 12 compounds:
|
B2O3
|
KMnO4
|
CuS
|
HCl
|
Na2O
|
CH3OH
|
|
H2CO3
|
NH3
|
Ba(OH)2
|
(NH4)2SO4
|
PCl5
|
FeCO3
|
Answer the following questions by writing the formulas of the
compounds in the space provided below. Write NONE if no compound in
the list is an answer to the question. Note: Some of the compounds
may be used more than once, others may not be used at all.
DO NOT GUESS! score = 0.5 x (# right - # wrong/2)
Which compound is a strong acid? HCl
Which compound is a weak acid? H2CO3
Which compound is an acidic oxide?
B2O3
Which compound is a basic oxide? Na2O
Which compound is a strong base? Ba(OH)2
Which compound is a weak base? NH3
Which compound is an oxidizing agent? KMnO4
Which two compounds are soluble salts? KMnO4,
(NH4)2SO4
Which two compounds are insoluble salts? CuS,
FeCO3
Which compound produces a gas when it reacts with sodium
hydroxide? (NH4)2SO4
(b) (4 marks). Write balanced equations for the following
chemical reactions. If there is no reaction, say so. Use the symbols
(s), (l), (aq), and (g) to designate solid, liquid, aqueous solution,
or gas.
(i) reaction of aluminum hydroxide and an aqueous solution of
nitric acid
Al(OH)3 (s) + 3 HNO3 (aq)
---> Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3 H2O
(l)
(ii) reaction of aqueous solutions of barium chloride and sodium
sulfate
BaCl2 (aq) +
Na2SO4 (aq) ---> BaSO4 (s) + 2
NaCl (aq)
(iii) reaction of magnesium metal and an aqueous solution of
hydrochloric acid
Mg (s) + 2 HCl (aq) ---> MgCl2 (aq) +
H2 (g)
(iv) reaction of aqueous solutions of iron(III) sulfate and
potassium hydroxide
Fe2(SO4)3 (aq) + 6
KOH (aq) ---> 2 Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3
K2SO4 (aq)
3. (10 marks)
(a) (3 marks) If a 0.2975-g sample of an unknown diprotic
acid requires 19.77 mL of 0.2005 M NaOH for titration to the
phenolphthalein end point, what is its molar mass? Diprotic acids
have the general formula H2A.
Equation: H2A + 2 NaOH --->
Na2A + 2 H2O
From titration data, moles of H2A = 1.9819 x
10-3, therefore molar mass is
0.2975 g/1.9819 x 10-3 mol = 150.1 g/mol
(b) (7 marks) The organic acid in part (a) above contains
the elements C, H, and O. If 0.4386 g of the acid yields 0.5144 g
CO2 and 0.1580 g H2O in a combustion analysis,
what are its empirical and molecular formulas?
|
CO2 44.01 g/mol
|
H2O 18.02 g/mol
|
Get masses of C and of H from the masses of CO2 and
H2O, respectively. Subtract them from the mass of the
original sample (0.4386 g) to obtain the mass of O.
mass of C = 0.1404 g
mass of H = 0.01768 g
mass of O = 0.4386 g sample - 0.1404 g C - 0.01768 g H = 0.2805
g O
Now calculate moles and proceed as usual:
|
C
|
H
|
O
|
|
1.169 x 10-2 moles C
|
1.754 x 10-2 moles H
|
1.753 x 10-2 moles O
|
Empirical formula = C2H3O3
with a molar mass of 75 g/mol. This is half of the value
calculated in part (a), so the molecular formula is
C4H6O6.
4. (10 marks)
(a) (6 marks) Fill in the blanks with the correct answer.
Barium is in Group 2A (give
number) and has 2 (give number) valence
electrons. Thus the barium cation will have a charge of
+2 . Nitrogen is in Group 5A
and has 5 valence electrons. Thus the
nitride ion will have a charge of -3. The
formula of barium nitride is
Ba3N2.
An isotope of element X has 25 protons and 27 neutrons in its
nucleus. Thus the atomic number of element X is
25 and its mass number is
52.Thus element X is Mn
(give symbol). The +2 cation of this element would have
23 electrons. A different isotope of element
X could have 25 protons in its nucleus
and a mass number of 50, 51, 53, etc..
A mole of sulfur tetrafluoride, SF4, contains
one mole(s) of sulfur atoms and
4 mole(s) of fluorine atoms. One molecule of
sulfur tetrafluoride has a mass of 1.794 x
10-22 grams. A sample of sulfur tetrafluoride in
which there are 1.00 x 1023 atoms of fluorine contains
2.50 x 1022 atoms of sulfur, and corresponds
to 0.0415 moles of sulfur tetrafluoride.
The formula of sodium pyrophosphate is
Na4P2O7. Thus the charge on the
pyrophosphate ion is -4 (give sign and number)
and the oxidation number of phosphorus is +5.
Chlorine dioxide, which is a major bleaching agent
used in the pulp and paper industry, is made from sodium chlorate and
sulfur dioxide according to the reaction
2 NaClO3 + SO2 --->
Na2SO4 + 2 ClO2
In this reaction, NaClO3 is
reduced because the oxidation number of Cl
changes from +5 in the reactant to
+4 in the product. The oxidizing agent in
this reaction is NaClO3.
(b) (4 marks) Explain the difference between the terms,
equivalence point and end point of a titration. Use the permanganate
titration of iron as an example. The net ionic equation for the
reaction in this titration is
5 Fe2+ + MnO4- + 8
H+ ---> 5 Fe3+ + Mn2+ + 4
H2O
In the permanganate titration, a solution of
KMnO4 is added to the solution containing Fe2+.
The equivalence point occurs when exactly enough permanganate
has been added to react with all the Fe2+, i.e. one mole
of MnO4- for every 5 moles of Fe2+.
The end point occurs when you can see the pink color due to excess
unreacted MnO4-. In this titration, the end
point occurs after the equivalence point.
Question 5 (8 marks)
(a) (2 marks) What do the letters VSEPR stand for? Use
VSEPR theory to explain why SO2 and CO2 do not
have the same shapes.
Valence Shell Electron
Pair Repulsion
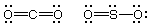
CO2 (16 electrons) is linear. The SO2 (18
electrons) molecule is bent because the extra electron pair on the
sulfur repels the bond pairs.
(b) (2 marks) State the Pauli Exclusion Principle. Show how
it applies to helium by giving a complete set of quantum numbers for
each electron in the helium atom.
No two electrons in an atom can have the same set
of four quantum numbers.
|
He
|
n
|
l
|
ml
|
ms
|
|
Electron 1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
+1/2
|
|
Electron 2
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
-1/2
|
The first three quantum numbers are the same for both electrons
but the 4th (ms) is different.
(c) (2 marks) Define the term, "first ionization energy."
Briefly explain why the first ionization energy of sodium is higher
than the first ionization energy of potassium but less than the first
ionization energy of magnesium.
11Na: [Ne]3s1
19K: [Ar]4s1
12Mg: [Ne]3s2
The first ionization energy of Na is lower than that of Mg
because Mg has more protons in its nucleus to attract the 3s electron
(a 3s electron is removed from each of these atoms, see electronic
configurations above.)
The first ionization energy of Na is higher than that of K
because the electrons are removed from s-orbitals with different
principal quantum numbers. A 4s electron in potassium is further from
the nucleus than a 3s electron in sodium, hence is easier to
remove.
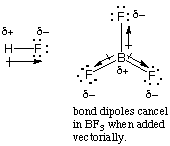
(d) (2 marks) What is the difference between a polar bond
and a polar molecule? Explain, using HF and BF3 as
examples in your explanation.
Both HF and BF3 have polar bonds because
the electronegativity of F is higher than that of H or B.
BF3 is nonpolar because the B-F bond dipoles in the
trigonal planar molecule cancel each other to give a net dipole
moment of zero. HF is polar because the bond dipole is the dipole
moment for HF.
6. (8 marks)
(a) (3 marks) The energy required to break C-C single bonds
is 348 kJ/mol.
(i) How much energy is required to break one C-C single bond?
5.78 x 10-22 kJ/bond
(ii) If ultraviolet radiation with wavelength 375 nm shines on a
compound containing C-C bonds, is there enough energy in one photon
to break a C-C bond? Explain your answer.
E = hc/lambda
= 5.30 x 10-19 J = 5.30 x 10-22 kJ
A photon with a wavelength of 375 nm doesn't have quite enough
energy to break a C-C bond.
(b) (5 marks) Use bond energies given below and estimate
the enthalpy change for the reaction of carbon monoxide and hydrogen
to produce acetic acid according to the following equation:
2 H2 + 2 CO --->
CH3CO2H
HINT: Draw the Lewis structures first! The connectivity of acetic
acid is
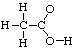
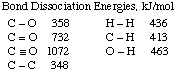
The Lewis Structures for the 3 molecules are:
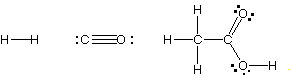
Thus, 2 moles of H2 bonds break, as do two moles of
C-O triple bonds. The energy to break the bonds is:
(2 mol H-H) x 436 kJ/mol + (2 mol C-O triple bonds)
x 1072 kJ/mol
= 3016 kJ to break the bonds.
The energy that is recovered when the product forms results
from the formation of three C-H bonds, one C-C bond, one C=O bond,
one C-O bond, and one O-H bond:
(3 mol C-H) x -413 kJ/mol
+ (1 mol O-H) x -463 kJ/mol
+ (1 mol C-C) x -348 kJ/mol
+ (1 mol C=O) x -732 kJ/mol
+ (1 mol C-O) x -358 kJ/mol
= -3140 kJ
Thus the expected enthalpy change is (energy required to break
bonds in reactants) + (energy given off when atoms form bonds in the
product)
= -124 kJ
7. (10 marks)
(a) Draw Lewis structures for the following molecules:
NH3, BrF3, CO2
NH3
# of valence e = ? 8
|
BrF3
# of valence e = ? 28
|
CO2
# of valence e = ? 16
|
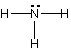
|
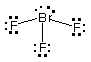
|
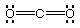
|
Of the molecules whose Lewis structures have been drawn above:
Which one(s) are polar? NH3,
BrF3
Which one(s) have no lone pairs on the central atom?
CO2
Which one(s) have a pyramidal molecular geometry?
NH3
Which one(s) have a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry?
NH3
(b Draw Lewis structures for the following ions:
ClO3-, NO3-,
ClF4+.
ClO3-
# of valence e = 26
|
NO3-
# of valence e = 24
|
ClF4+
# of valence e = 34
|
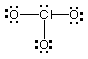
|
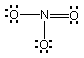
|
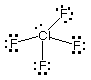
|
Of the ions whose Lewis structures have been drawn above:
Which one(s) have one lone pair on the central atom?
ClO3-, ClF4+
Which one(s) have a planar (trigonal or square) molecular
geometry? NO3-
Which one(s) have a trigonal bipyramidal electron-pair geometry?
ClF4+
Which one(s) have at least one bond angle of 109.5°?
ClO3-
MARKING SCHEME: Score = # right - #wrong/2
8. (24 marks; 1 mark each) Choose the best answer to each
of the following questions. Write the letter of the correct answer in
the space provided. Score = # right - #wrong/4
Answers are in bold print for each question.
According to the experiments concerned with the photoelectric
effect, what was the result of increasing the intensity of the light
striking the metal surface?
(a) the number of electrons emitted was
increased.
(b) The energy of the electrons emitted was increased.
(c) Both the number and energy of the electrons was increased.
(d) Both the number and energy of the electrons was decreased.
(e) There was no change in the number or energy of the electrons.
For a particular element, a photon of yellow light of wavelength
585 nm resulted when an electron fell from the third energy level to
the second energy level. From this information we can determine
(a) the energy of the n = 2 level.
(b) the energy of the n = 3 level.
(c) the sum of the energies of n = 2 and n = 3.
(d) the sum of the energies of n = 1, n = 2, and n = 3.
(e) the difference in energies between n = 2 and n = 3.
Which of the following electronic transitions in a hydrogen atom
would have the longest wavelength?
(a) n = 4 ---> n = 1
(b) n = 4 ---> n = 2
(c) n = 2 ---> n = 1
(d) n = 4 ---> n = 3
(e) n = 3 ---> n = 2
Which of the following electronic transitions in a hydrogen atom
would have the greatest energy?
(a) n = 4 ---> n = 1
(b) n = 4 ---> n = 2
(c) n = 2 ---> n = 1
(d) n = 4 ---> n = 3
(e) n = 3 ---> n = 2
What type of orbital is designated n = 3, l = 2, ml = 0?
(a) 2s
(b) 3s
(c) 3p
(d) 3d
(e) 3f
What is the maximum number of orbitals possible when l = 1?
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
(e) five
The quantum number l represents the
(a) number of valence electrons.
(b) number of orbitals.
(c) shape of the orbital.
(d) orientation of the orbital.
(e) momentum of the electron.
Which one of the following atoms is paramagnetic?
(a) P
(b) Mg
(c) Zn
(d) Ar
(e) Ba
The number of unpaired electrons in a manganese atom and a
manganese(II) ion, are, in order:
(a) 0,0
(b) 3,3
(c) 3,5
(d) 5,3
(e) 5,5
Which of the following is the correct electronic configuration for
the iron(III) ion?
(a) [Ar]3d5
(b) [He]2s22p2
(c) [Kr]4d105s25p2
(d) [Ar]3d34s2
(e) [Ar]3d64s2
Which of the following atoms is the largest?
(a) As
(b) Br
(c) F
(d) Sb
(e) Se
Which of the following atoms has the smallest first ionization
energy?
(a) Al
(b) P
(c) Sr
(d) Ga
(e) Rb
If metallic character is characterized as the ability to lose
electrons easily, the most metallic of the elements Ba, Mg, Pb, Sn,
and Zn is
(a) Ba
(b) Mg
(c) Pb
(d) Sn
(e) Zn
Of the ions K+, Ca2+, S2-, and
Cl-, which one (if any) has the largest ionic radius?
(a) K+
(b) Ca2+
(c) S2-
(d) Cl-
(e) they all have the same radius
Which of the following compounds would be expected to have the
highest melting point?
(a) LiF
(b) LiCl
(c) NaBr
(d) CsF
(e) CsI
Which of the following compounds would be expected to have the
longest ionic bond distance?
(a) LiF
(b) LiCl
(c) NaBr
(d) KBr
(e) KI
Which of the following is NOT a correct Lewis structure?
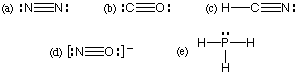
Answer: (d)
Which of the following is (are) CORRECT resonance structures for
the formate ion, HCO2&endash;?
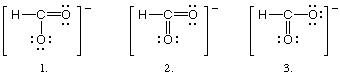
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
(e) 1, 2, and 3
Which of the following is (are) CORRECT resonance structures for
the N2O molecule?
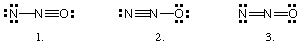
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 2 only
(e) 1, 2, and 3
What species does the following Lewis structure represent?
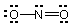
(a) NO2
(b) NO2+
(c) NO2-
(d) both NO2+ and NO2-
(e) NO2, NO2+ and
NO2-
Which statement is true regarding bond order, bond length, and
bond energy?
(a) As the bond order increases, the bond length
increases.
(b) As the bond order increases, the bond length decreases.
(c) As the bond order increases, the bond energy decreases.
(d) As the bond energy increases, the bond length increases.
(e) As the bond energy increases, the bond order decreases.
What is the formal charge on each atom in the following structure
for the nitrite ion?
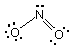
(a) Nitrogen is 2-, oxygen on the left is 1-, oxygen
on the right is 0.
(b) Nitrogen is 3+, both oxygens are 2-.
(c) Nitrogen is 0, oxygen on the left is 1-, oxygen on the
right is 0.
(d) Nitrogen is 0, oxygen on the left is 0, oxygen on the right is
1-.
(e) Nitrogen is 3-, oxygen on the left is 1-, oxygen on the right
is 2-.
From a consideration of the Lewis structure shown below, what is
the formal charge on sulfur in the molecule SO3?
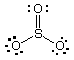
(a) 0
(b) 2+
(c) 2-
(d) 4+
(e) 6+
A measure of the ability of a gaseous atom to acquire an electron
to become negatively charged is called its
(a) ionization energy
(b) polarizability
(c) electron affinity
(d) electronegativity
(e) electron density
Back
to CHEM 1P80 Home Page
This page is
http://chemiris.labs.brocku.ca/~chemweb/courses/chem180/CHEM1P80_Final_1998.html
Created November 21, 2000 by M. F. Richardson
© Brock University, 2000