Reaction 
Cl2O (g) + F2O (g) ---> 2 ClF (g) + O2 (g)
-167.4 Cl2O (g) + 3 F2O (g) ---> 2 ClF3 (g) + 2 O2 (g)
-341.4 2 F2 (g) + O2 (g) ---> 2 F2O (g)
-10.4
(i) What is the oxidation number of Cl in Ca(OCl)2? +1
(ii) What is the oxidizing agent? Ca(OCl)2 (ox. no. of Cl changes from +1 in Ca(OCl)2 to -1 in CaCl2)
(iii) What is the reducing agent? NH3 (ox. no. of N changes from -3 in NH3 to -2 in N2H4)
(iv) Which reactant is oxidized? NH3
(v) Which reactant is reduced? Ca(OCl)2
(b) (6 marks) The net ionic equation for the reaction of strong acids with carbonate salts is
2 H+ (aq) + CO32&endash; (aq) ---> CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
What volume (mL) of a 0.2876 M hydrochloric acid solution is required to react with 0.2548 g of pure sodium carbonate? The molar mass of Na2CO3 is 106.0 g/mol.
Moles of HCl needed:
(0.2548 g Na2CO3) x (1 mol /106.0 g) x (1 mol CO32-/ mol Na2CO3) x (2 mol H+ / mol CO32-) x (1 mol HCl / mol H+)
= 4.8075 x 10-3 mol HCl needed.
Volume of HCl needed:
( 4.8075 x 10-3 mol HCl) x (1 L HCl / 0.2876 mol HCl) x (1000 mL/L)
= 16.72 mL
2. (13 marks) (a) (7 marks) Given the heats of the following reactions:
Reaction 
Cl2O (g) + F2O (g) ---> 2 ClF (g) + O2 (g)
-167.4 Cl2O (g) + 3 F2O (g) ---> 2 ClF3 (g) + 2 O2 (g)
-341.4 2 F2 (g) + O2 (g) ---> 2 F2O (g)
-10.4
Calculate the heat of the reaction of chlorine monofluoride with F2 according to the equation:
ClF (g) + F2 (g) ---> ClF3 (g)
Reaction 
2 ClF (g) + O2 (g) ---> Cl2O (g) + F2O (g)
167.4 Cl2O (g) + 3 F2O (g) ---> 2 ClF3 (g) + 2 O2 (g)
-341.4 2 F2 (g) + O2 (g) ---> 2 F2O (g)
Add reactions and enthalpy changes: -43.4 ------------------------------------------------ 2 ClF (g) + 2 F2 (g) ---> 2 ClF3 (g) --------- -217.4
Thus, for ClF (g) + F2 (g) ---> ClF3 (g), the enthalpy change is -217.4 kJ/2 = -108.7 kJ
(b) (6 marks) An 18.5-g sample of copper is heated to 99.5oC and then dropped into 58.5 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter. The temperature of the water rises from 24.0oC to 26.1oC. Calculate the specific heat of copper. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g.oC.
qwater + qcopper = 0
qwater = (58.5 g H2O) x (4.184 J/g.oC) x (26.1oC - 24.0 oC)
= 514 J
qcopper = - qwater = -514 J = (18.5 g Cu) (CCu) (26.1oC - 99.5 oC)
CFe = 0.38 J/ g.oC
3. (12 marks) Beer is made by fermenting a solution called "wort" that contains maltose (malt sugar, C12H22O11). Maltose ferments to ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and carbon dioxide according to the following equation:
C12H22O11 + H2O ---> 4 CH3CH2OH + 4 CO2
You have 25.0 L of wort with a density of 1.052 g/mL; it contains 8.80 wt. % maltose.
(a) (8 marks) What mass of ethanol will be produced by complete fermentation of the maltose?
Molar masses: CH3CH2OH 46.07 g/mol; C12H22O11 342.3 g/mol
Mass of maltose:
(25.0 L wort) x (1000 mL/L) x (1.052 g/mL) x (8.80 g maltose/100 g wort)
= 2314 g
Moles maltose = 2314 g fructose x 1 mol / 342.3 g
= 6.760 mol maltose
Mass ethanol:
(6.760 mol maltose) x (4 mol ethanol / mol maltose) x (46.07 g ethanol /mol)
= 1.25 x 103 g ethanol (rounded from 1246 g)
(b) (4 marks) If the final volume of beer is 24.2 L and its density is 1.10 g/mL, what is the percentage (by mass) of ethanol in the beer?
Mass of beer: 24.2 L x (1000 mL / L) x (1.10 g / mL) = 2.662 x 104 g
Percentage ethanol = (1246 g ethanol / 26620 g beer) x 100 = 4.68 %
4. (12 marks, 2 each)
(a) What is a salt? Give two examples of salts.
A salt is an ionic compound with cations other than H+ and anions other than OH- or O2-. One way to prepare salts is by an acid-base reaction in which the cation from the base and the anion from the acid.
Ca(OCl)2, Na2CO3, Fe(ClO4)3, CuCO3, FePO4, and Al(NO3)3 are some salts whose formulas can be found on this exam.
(b) Define specific heat (words, not an equation!) What are its units?
Specific heat is the heat required to increase the temperature of one gram of a substance by 1 oC. (or by 1 oK since temperature differences are measured.) The usual units are J / g.oC or J / g.oK.
(c) Define molarity (words, not an equation!) What are its units?
Molarity is the number of moles of solute in one liter of solution.
Units are mol solute/L solution, or more simply mol/L
(d) Define the heat of fusion. What are its units?
The heat of fusion is the energy required to melt a given quantity of solid to a liquid at the same temperature (the melting point). Units are J/g, kJ/g, kJ/mol, etc.
(e) What is the difference between Avogardro's number and the molar mass?
Avogadro's number is the number of things in one mole, the molar mass is how much one mole weighs. The "things" can be atoms of carbon in a mole of graphite, molecules of water in a mole of water, etc. A mole of anything contains 6.022 x 1023 fundamental units of that thing.
(f) What is the difference between isotopes and allotropes? Explain by using the element carbon as an example.
Isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number (same # of protons, therefore atoms of the same element), but different mass numbers and therefore different masses because the number of neutrons is different. Common isotopes of carbon include 12C (6p 6n), 13C (6p, 7n), and 14C(6p, 8n).
Allotropes are different forms of an element in the same physical state. Allotropes of carbon include graphite, diamond, buckyballs, and nanotubes, all of which consist of carbon only.
5. (15 marks)
Consider these 10 compounds:
(a) H2CO3 (b) Al(NO3)3 (c) MgO (d) FePO4 (e) HClO4
(f) CuCO3 (g) NH3 (h) Ba(OH)2 (i) N2O5 (j) Fe(ClO4)3
Answer the following questions by giving the formulas of the compounds in the space provided below. Write NONE if no compound in the list is an answer to the question. Score = # right &endash; # wrong/2!
Which compound is a weak base? NH3
Which compound is a strong base? Ba(OH)2
Which compound is a strong acid? HClO4
Which compound is a weak acid? H2CO3
Which two compounds are insoluble salts? FePO4, CuCO3
Which two compounds are soluble salts? Al(NO3)3, Fe(ClO4)3
Which compound is an acidic oxide? N2O5 (gives HNO3 upon reaction with water)
Which compound is a basic oxide? MgO (gives Mg(OH)2 upon reaction with water)
Which two compounds dissolve in water to give weakly conducting solutions? NH3, H2CO3 (weak electrolytes because one is a weak base and the other a weak acid)
Which compound is a nonelectrolyte when dissolved in water? NONE
Give the formulas of two compounds that react with each other to produce a gas. CuCO3 and HClO4 (carbonates react with acids to give carbon dioxide)
Main mistake in this question:
Inability to tell the difference between salts, acids, bases, and oxides (e.g. K2O, Ba(OH)2, and H3PO4 were said to be salts; H3PO4 and BaSO4 were said to be oxides, Cl2O7 was said to be an acid, etc.
Other important mistakes made in this question:
Mistakes in applying the solubility rules; not remembering which acids and bases are strong and which ones weak; not remembering which oxides are acidic and which ones are basic; not recognizing strong and weak electrolytes.
Final exam will have a question like this one! If you score better on this question type on the final than you did on this exam, I will replace your mark on this midterm.
6. (12 marks) (a) (5 marks)
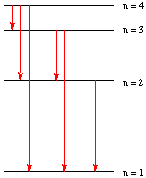
Assume that the diagram on the right represents the quantum levels of a hydrogen atom.
a. Considering only the four levels shown, how many different electronic transitions are possible when electromagnetic radiation is emitted by a hydrogen atom? 6 (as shown in red on the diagram)
b. Which of these transitions will have the longest wavelength?
n = 4 to n = 3
c. Which of these transitions will have the nighest frequency?
n = 4 to n = 1
(b) (7 marks) The energy required to break C&endash;C single bonds is 463 kJ/mol.
(i) (2 marks) How much energy (in Joules) is required to break one C&endash;C single bond?
(463 kJ/mol bonds) x (1000 J/kJ) x (1 mol bonds / 6.022 x 1023 bonds)
= 7.69 x 10-19 J/bond
(ii) (4 marks) What is the energy of one photon of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength 317 nm?
wavelength = 317 nm x (1 m /109 nm) = 317 x 10-9 m
= (6.626x 10-34 J.s) x (2.998 x 108 m/s) / (317 x 10-9 m)
= 6.27 x 10-19 J
(iii) (1 mark) If this radiation shines on a compound containing C&endash;C bonds, is there enough energy in one photon to break a C&endash;C bond? Explain your answer.
No. 7.69 x 10-19 J is needed to break one C-C bond, and the radiation supplies less than this amount in each photon (6.27 x 10-19 J).
7. (24 marks; 2 marks each) Choose the best answer to each of the following questions. Write the letter in the space provided for the answer. Write your letters clearly!
Marking scheme: 2 x (# right - # wrong/4)
(i) The classification of the following reactions in order is
HCl (g) + NH3 (g) ---> NH4Cl (s)
2 HgO (s) ---> O2 (g) + 2 Hg (l)
HCl (aq) + AgNO3 ---> HNO3 (aq) + AgCl (s)
(a) acid-base, precipitation, and redox, respectively
(b) precipitation, redox, and acid-base, respectively
(c) redox, precipitation, and acid-base, respectively
(d) acid-base, redox, and precipitation, respectively
(e) redox, acid-base, and preciptation, respectively
(ii) Identify the spectator ion or ions (if any) in the precipitation reaction of iron(III) sulfate with barium chloride:
(a) Ba2+ and SO42&endash;
(b) Ba2+ and S2&endash;
(c) Fe2+ and Cl&endash;
(d) Fe+ and Cl&endash;
(e) there are no spectator ions in this reaction
(iii) Which process involves the largest energy change for one mole of acetic acid?
(a) Delta Hsublimation
(b) Delta Hcondensation
(c) Delta Hboiling
(d) Delta Hmelting
(e) Delta Hvaporization
(iv) Consider the thermal energy transfer during a chemical process. When the system transfers heat to its surroundings, the process is said to be ___ and the sign of q is ___.
(a) exothermic, positive
(b) endothermic, positive
(c) endothermic, negative
(d) exothermic, negative
(e) enthalpic, negative
(v) What is Delta E for a system which has the following two steps:
Step 1: The system absorbs 60 J of heat while it does 30 J of work.
Step 2: The system releases 40 J of heat while 50 J of work is done on it.
(a) 40 J
(b) 20 J
(c) zero J
(d) -20 J
(e) -40 J
(vi) Which of the following equations represents an enthalpy change at 25°C and 1 atm that is equal to Delta Hof?
(a) 1/2 C (s) + 1/2 CO2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) ---> CH3OH (l)
(b) CO (g) + 2 H2 (g) ---> CH3OH (l)
(c) C (s) + 1/2 O2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) ---> CH3OH (l)
(d) 2 C (s) + O2 (g) + 4 H2 (g) ---> 2 CH3OH (l)
(e) C (s) + H2O (l) + H2 ---> CH3OH (l)
(vii) The standard enthalpy of formation of silicon dioxide (quartz) is represented by the equation
From this information, we can conclude that silicon dioxide
1. is energetically unstable with respect to its elements
2. will be formed rapidly from silicon and oxygen
3. will release energy when prepared from its elements
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 2 only
(e) 2 and 3 only
(viii) If 4.00 g of element A reacts completely with 8.00 g of element B, which of the following statements must be true?
(a) The reaction requires 4 moles of A to react with 8 moles of B
(b) The formula of the product is AB2.
(c) The atomic weight of A is double the atomic weight of B.
(d) The atomic weight of B is double the atomic weight of A.
(e) The maximum mass of product that can be formed is 12.00 grams.
(ix) What is the mass number of an atom of iodine with 73 neutrons?
(a) 53
(b) 126
(c) 126.904
(d) 127
(e) 180.95
(x) Which group of compounds are ALL ionic?
(a) H2CO3, NaCl, FeS
(b) KCl, NH4Cl, AgCl
(c) NaCl, AlCl3, CH3Cl
(d) K2O, Fe2O3, P4O10
(e) Ba(OH)2, NaOH, ClOH
(xi) What would be the best description of Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect?
(a) Electrons have a definite mass.
(b) Ejection of photons occurs when the intensity of light increases beyond a certain minimum.
(c) Light consists of "particles" with a definite mass.
(d) Light consists of "particles" with a definite energy.
(e) Ejection of electrons occurs when the energy of the photon is greater than a certain minimum.
(xii) A chemist places CaCO3 in one flask and KBr in another. Water is added to both flasks and the mixture in the first flask is added to the second. Which choice below correctly describes the results?
(a) Both of the compounds in the flasks dissolve when water is added, and CaBr2 precipitates when the contents of the two flasks are mixed.
(b) Both of the compounds in the flasks dissolve when water is added and there is no reaction when the contents of the flasks are mixed.
(c) The CaCO3 does not dissolve in water, but the KBr does dissolve. There is no change when the contents of the flasks are mixed.
(d) The KBr does not dissolve in water but the CaCO3 does dissolve. There is no change when the contents of the flasks are mixed.
(e) none of these
This page is
http://chemiris.labs.brocku.ca/~chemweb/courses/chem180/Midterm_2B_2000.html
Created November 19, 2000 by M. F. Richardson
© Brock University, 2000