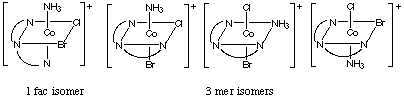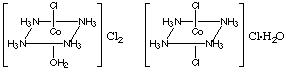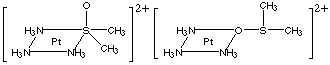CHEM 2P32 Hints for Assignment 3
1. Draw Lewis structures for each of the following ligands.
thiocyanate, SCN-
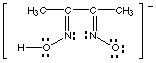
dimethylglyoximate anion
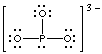
phosphite, PO33-
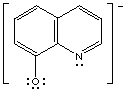
8-hydroxyquinolinate (oxime)
Answers and Some Comments
Draw Lewis structures for simple ions like thiocyanate and
phosphite in the usual way. Note that strong C-N pi-bonding leads to the
triple bond in SCN-, instead of a structure containing two double
bonds.
The phosphite ion has no double bonds to phosphorus. The Lewis structure
shown has an octet about the phosphorus, and the formal charges all reside
on the most electronegative atoms.
Dimethylglyoxime and 8-hydroxyquinoline structures are shown on the
handout, "Structures and Abbreviations of Some Common Organic Ligands."
Count the electrons around each atom and add electron pairs until the octet
rule is satisfied.
thiocyanate
|
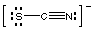
|
dimethylglyoximate
|
|
phosphite
|
|
8-hydroxyquinolinate
|
|
2. Refer to your Lewis structures in Question 1 above.
(a) Give the name(s) of the ambidentate ligands.
(b) Give the name(s) of the chelating ligands.
Answers and Reasons
Thiocyanate and phosphite are ambidentate. Thiocyanate can
bond either through sulfur or through nitrogen (there are lone pairs on
both). Phosphite can bond either through phosphorus or oxygen (there are
lone pairs on both).
Dimethylglyoximate and 8-hydroxyquinolinate are chelating ligands. Dimethylglyoximate
can form 5-membered rings by bonding to a metal through its two nitrogens,
8-hydroxyquinolinate by bonding through the nitrogen and oxygen.
3. (a) Draw 2 geometric isomers for the ion whose formula is [Co(dien)(NH3)ClBr]Cl
(b) Draw 2 optical isomers for the compound whose formula is
[Co(dien)(NH3)ClBr]Cl
(c) Draw 2 ionization isomers for the compound whose formula is [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl.H2O
(d) Draw 2 linkage isomers for the compound whose formula is [Pt(NH3)3(Me2SO)]Cl2
("Me" is the abbreviation for the methyl group, CH3)
Answers
(a) Any two of the isomers shown below:
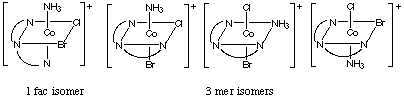
(b) The only isomer above that does not have a plane of symmetry is
the fac isomer above. Draw it and its mirror image.
(c) Exchange a water molecule with a chloride ion in the compound to
produce an ionization isomer (ammonia is not normally exchanged). Thus:
[Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl.H2O and [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]Cl2.
The complex ions of both these compounds exist as cis and trans isomers.
A sketch of either cis or trans would be acceptable; the trans isomers
are shown below.
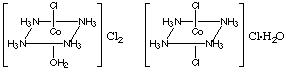
(d) Dimethylsulfoxide is ambidentate. Structures:
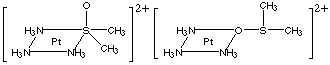
4. Six structures are shown below. Give the letters of the two that
are identical (same enantiomer) as the structure in Figure A.
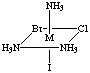
Fig. A
|
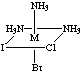
Fig. B
|
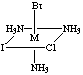
Fig. C
|
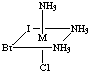
Fig. D
|
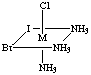
Fig. E
|
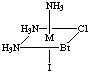
Fig. F
|
Answers B and E are the same as A. Unless you have exceptional powers
of 3-D visualization from a 2-D figure, you will need to build a model
(or two models, enantiomers of each other) and compare to the figures.
5. Give formulas for the following ions or compounds. Use standard
abbreviations for the organic ligands.
(a) hexaaquotitanium(III) ion
(b) hexafluoromolybdate(III) ion
(c) tricarbonylnitrosyl(triphenylphosphine)manganese(0)
(d) tris(o-phenanthroline)vanadium(III) ion
(e) diamminegold(I) ion
(f) dicyanoargentate(I) ion
(g) (ethylenediaminetetraacetato)manganate(II) ion
(h) pentaammine-N-nitritocobalt(III) ion
(i) hexaammineiron(III) sulfate
Answers You have to know three things to give a formula when given
the name or vice versa
1. The names, formulas, and charges of the ligands (and their
abbreviations if they are organic)
2. The names of the metal ions
3. The charge on the complex is equal to the sum of the charges on the
metal ions and the ligands
(a) hexaaquotitanium(III) ion
|
[Ti(H2O)6]3+ |
(b) hexafluoromolybdate(III) ion
|
[MoF6]3- |
(c) tricarbonylnitrosyl(triphenylphosphine)manganese(0)
|
[Mn(CO)3(NO)(Ph3P)] |
(d) tris(o-phenanthroline)vanadium(III) ion
|
[V(o-phen)3]3+ |
(e) diamminegold(I) ion
|
[Au(NH3)2]+ |
(f) dicyanoargentate(I) ion
|
[Ag(CN)2]- |
(g) (ethylenediaminetetraacetato)manganate(II) ion
|
[Mn(EDTA)]2- |
(h) pentaammine-N-nitritocobalt(III) ion
|
[Co(NH3)5NO2]2+ |
(i) hexaammineiron(III) sulfate
|
([Fe(NH3)6])2(SO4)3 |
6. Give the correct IUPAC name for ions or compounds having the
following formulas:
(a) [PtCl2(C2H4)2]
(b) [Cr(en)3]3+
(c) K2[Ni(CN)4]
(d) [Zn(NCS)4]2-
(e) [Co(gly)3]
(f) ([Co(NH3)4(SCN)2]2SO4
(g) [Au(CN)4]-
(h) [Cu(acac)2]
(i) [FeCl4]-
Answers
(a) [PtCl2(C2H4)2]
|
dichloro(ethylene)platinum(II) |
(b) [Cr(en)3]3+
|
tris(ethylenediamine)chromium(III) ion |
(c) K2[Ni(CN)4]
|
potassium tetracyanonickelate(II) |
(d) [Zn(NCS)4]2-
|
tetra-N-thiocyanatozincate ion |
(e) [Co(gly)3]
|
tris(glycinato)cobalt(III) |
(f) ([Co(NH3)4(SCN)2]2SO4
|
tetraamminedi-S-thiocyanatocobalt(III) sulfate |
(g) [Au(CN)4]-
|
tetracyanoaurate(III) ion |
(h) [Cu(acac)2]
|
bis(acetylacetonato)copper(II) |
(i) [FeCl4]-
|
tetrachloroferrate(III) ion |
Back
to Chem 2P32 Home Page
Back
to Assignment Schedule
This page is http://chemiris.labs.brocku.ca/~chemweb/courses/chem232/CHEM_2P32_Assign_3.html
Last revised: January 12 2001 by M. F. Richardson
© Brock University, 2001