|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. (10 marks)
(a) Give the oxidation numbers for iodine in each of the following compounds:
(i) MgI2: The oxidation number of iodine is ______.
(ii) IO65-: The oxidation number of iodine is ______.
(iii) I2O5:
The oxidation number of iodine is ______.
(b) Given the following equation:
Cr2O72-(aq) + 3 Sn2+(aq) + 14 H+ (aq) ==> 2 Cr3+ (aq) + 3 Sn4+(aq) + 7 H2O (l)
(i) What is the oxidizing agent?
(ii) What is the reducing agent?
(iii) Which reactant is oxidized?
(iv) Which reactant is reduced?
2. (20 marks)
(a) (3 marks) How many mL of 3.00 M KOH are
needed to make 0.500 L of 0.840 M KOH? (molar mass of KOH = 56.1 g/mol)
(b) (3 marks) What is the molarity of sodium
ions in a solution that contains 0.0205 mol Na3PO4
in 0.500 L of solution? (The molar mass of Na3PO4
is 163.94 g/mol)
(c) (6 marks) (i) Write a balanced equation
for the reaction of HCl with Ba(OH)2.
(ii) If 37.2 mL of 0.107 M HCl are needed to titrate 50.0 mL of a Ba(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ba(OH)2 ?(d) (8 marks) Consider the reaction of ammonia with oxygen to produce nitrogen oxide and water according to the equation below. If 6 moles of NH3 and 8 moles of O2 are allowed to react, how many moles (if any) of each species are present after the reaction? Show your reasoning clearly!
4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) ==> 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (g)
| Reagents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. (25 marks)
(a) (10 marks) (i) Suppose you burn 1.500 g of benzoic acid, C7H6O2, in a combustion calorimeter and find that the temperature of the water in the calorimeter increases from 22.50 to 31.69°C. The calorimeter contains 775 g of water. Calculate the molar heat of combustion of benzoic acid. Assume that the calorimeter absorbs no heat.
Molecular weight of benzoic acid: 122.12 Heat capacity
of water: 4.18 J/g-K
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the combustion of one mole of benzoic acid.(b) (8 marks) Use the enthalpy change for the first two reactions to determine the enthalpy change for the third reaction.
| Reaction |
|
| N2(g) + 3 H2 (g) Æ 2 NH3 (g) |
|
| 2 H2(g) + O2 (g) Æ 2 H2O (g) |
|
| 2 N2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) Æ 4 NH3 (g) + 3 O2 (g) |
|
(c) (7 marks) Styrene, C8H8, is burned in a calorimeter to find the enthalpy change for the combustion reaction
C8H8 (l) + 10 O2 (g) ==> 8 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (l)
If the standard enthalpy change for this reaction is -4395.0 kJ, what is the standard molar enthalpy of formation of styrene?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. (10 marks)
Water is formed in a direct reaction of oxygen and hydrogen:
2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) ==> 2 H2O (g)The starting mixture is represented by the diagram, in which the black circles represent O and the white circles represent H.
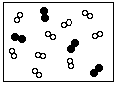
(a) Which of the following diagrams represents the product mixture? (Write in the number of the diagram)
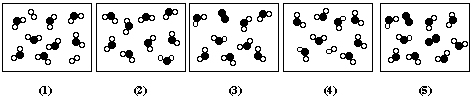
(b) Is one of the reactants limiting, or are
they present in the correct stoichiometric amount? Explain your answer.
5. (20 marks)
(a) (5 marks) The standard molar enthalpy
of formation of ethanol, C2H5OH
(l), is -277.7 kJ/mol. Write the balanced equation for which the
enthalpy of reaction is -277.7 kJ/mol.
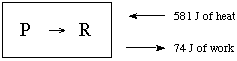
b. (10 marks) A reaction, P ==> R, absorbs 581 J of heat and does 74 J of work on its surroundings.
(i) What is q for the system?
(ii) What is w for the system?
(iii) What is q for the surroundings?
(iv) What is w for the surroundings?
(v) What is the internal energy change for the system?
c. (5 marks) Explain the terms "end point"
and "equivalence point" as they apply to the titration of iron(II) by permanganate.
6. (15 marks)
(a) (5 marks)
Assume that the diagram on the right represents the quantum levels of a
hydrogen atom (approximately to scale).
|
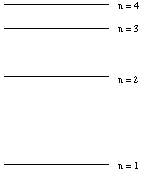 |
| (b) (10 marks) The diagram on the right shows three possible electronic transitions for an atom of an unknown element. Use the information given in the diagram and on page 1 of the exam, and determine the wavelength associated with Transition 3. | 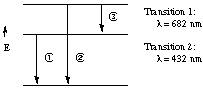 |